We look at some really helpful
built-in tools this week.
Finding and diagnosing problems in Windows,
whether that’s Windows 7 or 8, can be a frustrating affair if you don't really
know where to look in the first place. Naturally, there are many products and
third party programs out there to help you diagnose any problems you may have,
but the trick here know which are effective and which are more likely to cause
even more problems.
It’s a sad fact that there are unscrupulous
individuals out there who like nothing more than to prey on the unsuspecting in
the form of a program that's sold as being helpful, but in actual fact will
litter your system with unwanted rubbish. There is then a certain amount of
care needed when looking for a set of system tools to help solve any issues
with your PC, thankfully though, there are already a set of useful tools
available already on your system.
Windows Memory Diagnostic
Windows Memory Diagnostic is a tool that
can either restart your PC and test the installed memory for any problems, or
can be scheduled to check at the next reboot. It's very similar to the popular
MemTest86 program, and can be found in the Control Panel, under Administrative
Tools and by clicking the ‘Diagnose your computer’s memory problems’ link.
Alternatively, you could just type in ‘Windows Memory Diagnostic’ into the
Start button search, and follow the links from there.
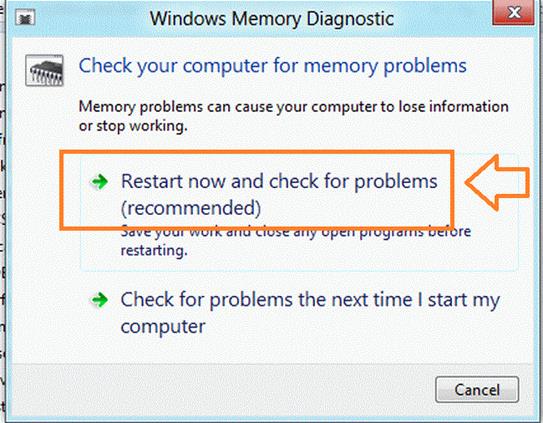
Start
Memory Diagnostic Tool in Windows 8
Interestingly, there are a few settings you
can adjust before the diagnostics start. When the tools starts, press F1 and
you'll be able to choose either Test Mix, which will offer you Basic, Standard
or Extended tests. Cache will offer the cache settings for each test, be that
Default, On or Off. Also, Pass Count will allow you to choose the number of
times the test is repeated. When you've made your advanced selection, hit F10
to start the tests.
Resource Monitor
The Windows Resource Monitor is quite an
impressive collection of detailed and useful information from the important
resources in your system. CPU, Memory, Hard Drives and Network details can all
be found under the relative titled tabs, with each one drilling down to show
the processes, modules, activity and a second by second account of all the
ins-and-outs of the computer.

Resource
Monitor
To open it up, either right-click the
Taskbar at the bottom of the screen and select Task Manager from the menu, then
click on the Performance tab followed by the ‘Resource Monitor...’ button at
the bottom of the window. Or, simply type in ‘resource monitor’ from the Start
button search and follow the link from there.
The graphs and details displayed may at first
be a little confusing, but take a moment or two and you'll soon come to see
what’s going on, and particularly where and what is taking up the more valuable
resources of the system. For example, the Network tab contains all sorts of
information that could help you solve the sudden connection problems you're
having. If there's a program that’s sucking up all the available bandwidth,
then you’ll find it in here and you can then ascertain as to whether it's just
a glitch that needs resolving, or something nasty has got into the system and
is using up all the resources.
This is an underused, yet remarkably
powerful tool that will help you diagnose any issues you're having with your
PC, or at the very least eliminate any alien and unwanted processes.
Performance Monitor
The built-in Windows Performance Monitor is
also an interesting tool, in that you can see and compare graphical data on
certain aspects of your system's resources over a period of time. It’s a tool
that was once used by system admins back in the old NT days, where the sewer
could be analyzed over a period of time to deduce what needed to be upgraded,
or what times it was most heavily used. These days, it can still be used for
that purpose, but essentially it can also be used in conjunction with the above
other tools to further break down the causes of a particular problem.
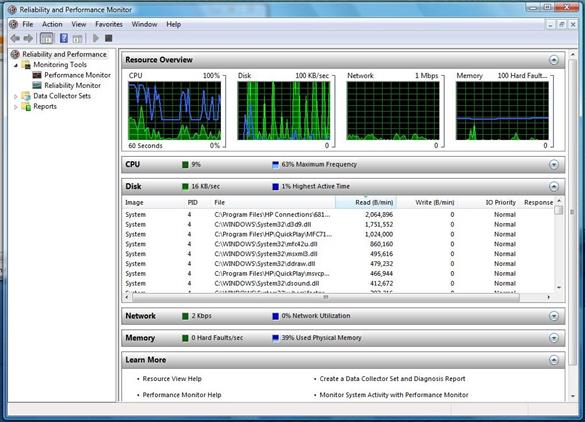
Reliability
and Performance Monitor
You can launch the Performance Monitor tool
by either right-clicking Computer from the Start button, then, Manage followed
by Performance and Performance Monitor, or by typing in Performance Monitor (or
Perfmon) into the Start button search box.
You can set the graph to view and collect
all sort of data from a variety of available counters, or system resources and
services. You can measure everything from .NET usage through to Processors,
Memory and Cache usage, to Windows Media Player Metadata usage. Furthermore,
the data collected can then be saved, exported, copied and pasted into any of
the popular Office suites or online tools for further analysis and detection of
any issues.
Again, Performance Monitor is a handy tool
that's often forgotten in favor of the more glamorous third party tools
available. It’s especially useful when determining how changes to the system
affect the overall performance, such as an increase in memory, or a tweak to an
overclocked CPU.
User Accounts
Problems with user accounts can be
difficult to diagnose, and the l usual User Accounts management tool within
Windows often leaves some much needed information out. In this case, you should
try the Advanced User Accounts tool, which offers a little more than the normal
utility.
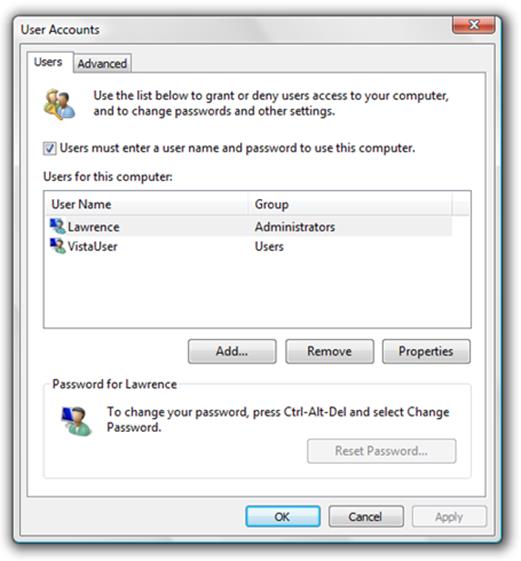
Advanced
User Accounts
The easiest way to open up the Advanced
User Accounts tool is to simply press Ctrl and the Windows Key, then type in
‘control userpasswords2’ into the Run box. From there, you'll gain access to
all sorts of useful information, such as the user names and relative groups,
password management, advanced user management and the ability to allow a single
user computer to log into Windows without having to go through the login
screen.
Basically, if you’re having problems with a
user account on your PC, perhaps permissions based, or you simply want to make
your boot up and log into Windows much easier (although far less secure), then
you’ll be able to find the necessary tools within the Users and Advanced tabs of
the Advanced User Accounts tool.
Conclusion
For most of the problems you'll come across
during your PC's life, these four free built-in tools will more than likely
help you determine what the causes are. Of course, if you need to drill further
down, then you’ll need something more specific, if the problem lies with your
graphics card for example. Generally, though, this little lot will go a long
way to helping out the average user with their computing problems.
Other built-in useful Windows tools
The four tools we mentioned here are just
some of the built-in utilities available for the standard Windows setup, if you
need something more particular, or you want to see what else is available, then
consider looking these up via the Start button search function.
Computer Management: the Microsoft Management Console contains pretty much everything
you'll ever need
Disk Cleanup:
helps clean up unwanted and temporary files to keep your system neat and tidy.
Edit Group Policy: although only available on the Pro and Ultimate versions of
Windows, this GPO tool can change many aspects of your system.
Regedit:
From here you can edit the Windows Registry and either tweak or kill your PC.
Msconfig: A
handy tool for selecting start up programs and tweaking the system.
System Information: Get all sorts of information on your hardware and software from
within here.
View Reliability History: A very useful tool for assessing your systems stability.