Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 2.4GHz, Miracast and more: Darien
Graham-Smith explains each of today's numerous wireless standards
RFID transmitters don’t necessarily need a
power source. The chip has such modest power demands that it can run off the
current induced by a nearby electromagnet (see Wireless power, p58), and this
can be built into the reader. Conversely, it’s possible to use powered RFID
tags that communicate with passive readers.
He
has developed a testbed to rapidly test new RFID tag prototypes
RFID supports an extremely wide range of
frequencies, from 120kHz up to 10GHz, with different transmission speeds and
different ranges; the most powerful active tags can be read at a range of up to
200m. RFID isn’t something you’d necessarily build into a personal computer or
smartphone, but it does have consumer applications: for example, you could
conceal an RFID tag inside the frame of a bike, and use it as evidence of
ownership if the bike is stolen.
A related technology is near-field
communication (NFC). This builds on RFID principles by adding two-way
communications capabilities: when two NFC devices are close enough to “see”
each other (conventionally established by tapping them together, although physical
contact isn’t needed), they can take it in turns to send and receive data.
NFC is built into an increasing number of
smartphones and tablets. In principle, it could be used to exchange files and
information between such devices.
In practice, NFC’s useful range of around
4cm (coupled with a slow maximum data rate of 424Kbits/sec) makes this
impractical. Implementations such as Android’s “Beam” feature typically use NFC
simply to exchange basic device information, which is then used to initiate a
faster and more robust link, such as Bluetooth. Similarly, Windows 8.1’s “c”
feature doesn’t actually transmit pages via NFC; the tag embedded in the
printer merely broadcasts its network path and driver details to a receiver.
This information can then be used to automatically configure the client so that
print jobs can be sent to the printer via conventional infrastructure.

NFC’s
useful range of around 4cm
Passive NFC tags are also used in retail,
enabling customers pay for goods from a digital wallet by tapping their
smartphone against an embedded tag. It’s basically the same idea as the
RFID-based payment systems mentioned above, but with the roles reversed so that
the active reader is provided by the customer. This makes it much cheaper and
easier for service providers to implement - all they have to do is program a
cheap, robust NFC tag with the appropriate charging details and affix it to a
flat surface.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is the world’s most popular ad
hoc wireless connection: today it’s built into most laptops, smartphones and
tablets. It works in the 2.4GHz band, like the keyboards and mice mentioned
above, but the standard is more sophisticated, including more than 30
“profiles” that allow Bluetooth-enabled devices to work together in different
ways.
A Bluetooth keyboard, for example, would
support the Human Interface Device (HID) profile, so a compatible operating
system would know it could receive input from it. A pair of wireless
loudspeakers would use the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP), meaning
the
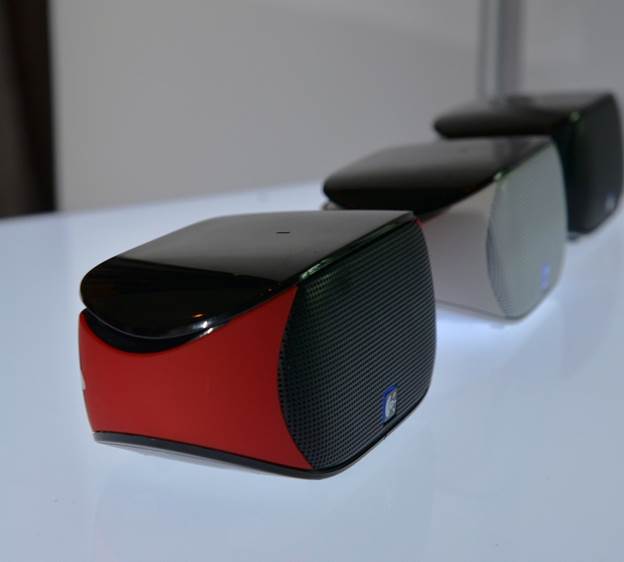

…devices
that support Bluetooth® Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP),
and works with phones that support Bluetooth Hands-Free Profile (HFP 1.5)
OS would recognise them as an audio output
device. Other defined Bluetooth profiles cover remote control for TVs and hi-fi
systems, file transfer, printing, speech transmission and network gateway
services - so you can, for example, tether a mobile phone to a laptop via
Bluetooth and share its 3G connection.