The difference between ‘Arrange By’ and
‘Sort By’
12. One way to sort files in Finder windows is to select View ð Arrange By, followed by a find criterion (‘Name’, ‘Kind’, ‘Date Added’, or
whatever). Your system will use that criterion to sort files and folders in the
parent folder you’re viewing. Later, when you add new files to the folder,
they’ll appear properly in the file hierarchy.
For less
long-lasting results, hold down the

To set the order in which files appear, select View ð Arrange By
2 methods for creating Aliases and
Symlinks
If you’ve been using a Mac for a while, you
know that an alias is a tiny file that points to – and acts as another.
For example, an alias on your desktop might provide quick access to a file
buried in your user folder.
As a Unix-based operating system, OS X also
supports symbolic links (also variously known as Symlinks and soft
links), which are essentially Unix’s version of aliases. You should
understand how they differ and how to create both.
Oversimplifying a bit, an alias acts as an
enduring reference to an item such as a file, a folder, or a volume. If you
move the target item, the alias will still point to it. If you rename the
target item, the alias will still point to it. OS X “remembers” the original
file.
As
a Unix-based operating system, OS X also supports symbolic links, which are
essentially Unix’s version of aliases
In contrast, a Unix symlink acts as a
reference to a particular location. (A symlink is a text file containing the
path to that particular location.) When the OS opens a symlink, it reads the
file path named in the text file and opens the file at that path. If you move
the target item, the symlink will no longer work. If you replace the target
item with another one with the same name, the symlink will point to that new
item.
Most OS X apps are built to work with
aliases. But if an app isn’t a native Mac app, it may see an alias as nothing
more than a useless little file. On the other hand, any app can work with
symbolic links: As far as the app is concerned, a symlink is its target file.
And if you want to replace the original file with a different version, a
symlink will still work, whereas an alias won’t.
One app that treats aliases and symbolic
links differently is Dropbox. If you put an alias to your personal Library
folder (yourusername/Library) in your Dropbox folder, the service will
treat it as a document and sync just the alias file. If instead you put a
symlink to that Library folder in your Dropbox folder, the service will treat
that symlink as your actual Library and thus sync the entire folder across your
computers. Now let’s look at how to create aliases and symbolic links.
- Create an alias Select the file in the Finder, and choose File ð Make
Alias (or press z-L, or right-click
or -click the file and select Make Alias from the
contextual menu).
- Create a symbolic link Open Terminal, and type ln -s
/path/to/original/file/filename /path/to/link/linkname. Let’s
say that you have a file named ‘testfile txt’ located in your Documents
folder, and you want to put a symlink to that file on your desktop. To do
so, type ln -s ~/Desktop/testfile.txt ~/Documents/testsymlink.txt.
(If you don’t specify a destination path, the symlink will by default
appear in the original file’s directory.). If you anticipate that you’ll
often be creating symlink, you can use SymbolicLinker, an OS X service
that automatically adds a Make Symbolic Link command to the Finder’s
Services menu.
6 ways to reclaim disk space
Running out of disk space? It’s easy to do,
especially on a laptop Mac that has limited flash storage available. When you
need more space for your apps and data, try taking these steps.
- Empty the Trash Simply dragging files to the Trash doesn’t free up the disk
space that they occupy. To clear the space completely, you must also
choose Finder ð Empty Trash. (Remember to go back
and empty the Trash again after performing the other tips in this list!)
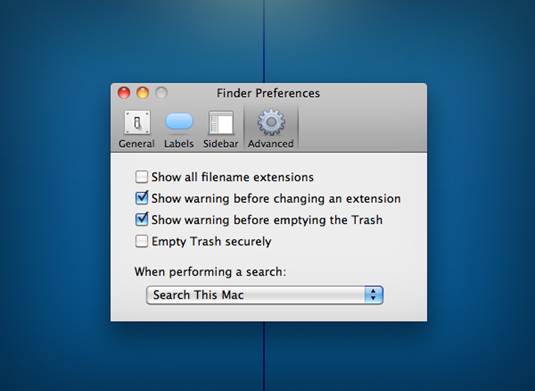
Simply
dragging files to the Trash doesn’t free up the disk space that they occupy
- Restart Restarting
can free up a bit of space by clearing virtual memory swap files, certain
caches, and a few other items.
- Clean out your Downloads folder Your Downloads folder (at the top level of your home folder, by
default) can easily become clogged with clutter. Drag anything you find
there that you no longer need to the Trash.
- Delete duplicates Don’t waste your Mac’s precious disk space storing multiple
copies of the same file. To find duplicates that you may not even know
existed, try a utility like Chipmunk ($17, go.macworld.com/chipmunk)
or Hyperbolic Software’s Tidy Up ($30, go.macworld.com/tidyup).
- Clear caches Caches generally help your Mac run faster, so deleting them can
slow it down and they’ll quickly rebuild themselves anyway. Still, in a crunch,
clearing caches might give you some breathing room. The easiest way to
find and safely delete caches I to employ a utility such as Titanium’s
Software’s OnlyX (donation requested; go.macworld.com/onyx).
Otherwise, you can navigate to your username/Library/Caches folder
and have at it. (If your Library folder isn’t showing, see macworld.com/a/1161156
for a few options.)
- Try an uninstaller Because many apps are not self-contained, a well-designed
uninstaller can help you find and delete all of the scattered pieces of
unwanted apps that came aboard your system.
‘Arrange By’ keyboard shortcuts
21. In any Finder window, you can press the
following keyboard combinations to sort files by different criteria.