Apache CouchDB
Apache CouchDB is an open source NoSQL
database. CouchDB uses JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, lightweight
data-interchange format) to store data. JavaScript is used as its query
language. CouchDB is published via the Apache Software Foundation in 2008. In
CouchDB, each database is a collection of independent documents. Each document
manages its own data and metadata (self-contained schema). CouchDB is ideal in
situations where a network connection is not guaranteed, due to its replication
and synchronization capabilities. The BBC uses it for its dynamic content
platforms. It can be used in applications such as CRM and CMS, where data is
changed occasionally, and versioning is crucial. Cloudant is an enterprise
software company that provides an open source distributed database service
based on the Apache CouchDB project.
This
is big news as this version includes Apache CouchDB, used as a replicable
database by desktop apps.
Its features are:
§
CouchDB provides ACID semantics by implementing
a form of Multi-Version Concurrency Control (high volume of concurrent readers
and writers without conflict).
§
CouchDB supports bi-directional replication (or
synchronization) and offline operation.
§
Unique URI that gets exposed via HTTP. REST uses
the POST, GET, PUT and DELETE HTTP methods for the four CRUD operations.
§
It assures eventual consistency (a model used in
the domain of parallel programming) to be able to provide both availability and
partition tolerance.
MongoDB
MongoDB is an open source, scalable,
high-performance, and document-oriented database optimized for highly transient
data, and is written in C++. It provides a RESTful API. A free cloud-based
monitoring service is provided for MongoDB deployments. It supports search by
range queries, fields and regular expressions. Master-slave replication is
supported, where the master can perform read and writes operations, while
slaves can read or take back-ups. MongoDB supports horizontal scaling with the
use of sharing. It can be effectively used as efficient file storage, which is
capable of taking the benefits of load balancing and data replication.
Use-cases:
§
Flexible schemas are the best fit for document
and content management systems.
§
Good fit in conjunction with RDBMS, for
e-commerce infrastructure.
§
Good fit for gaming, due to high read-write
performance.
§
Very efficient for server-side infrastructure of
mobile applications
Graph databases
Graph databases store graph-oriented data
with nodes – entities such as people, businesses, accounts and edges. They
connect nodes to nodes, or nodes to properties, and represent the relationship
and properties, where every element holds a direct pointer to its neighboring
element, and no index lookups are required. They are commonly used to store
associations in social networks. Graph databases are often faster for
associative datasets than traditional databases. They can scale logically to
large datasets, as they do not usually require costly join operations. They are
a powerful tool for graph-like queries, such as computing the shortest path
between two nodes in the graph.
Neo4j
Neo4j is an open source property graph
database implemented in Java. It stores data structured in graphs. The graph-based
model makes Neo4j highly agile and fast. It is massively scalable, up to
several billion nodes, and highly available when distributed across multiple
nodes. It can be easily embedded by including the Neo4j library JARs in your
build. Neo4j in high-availability mode has a single master and zero, or more
slaves and can handle write requests on all machines, so there is no need to
redirect those to the master. A slave can handle writes by synchronizing with
the master to maintain consistency. All updates propagate from the master to
other slaves in due course, so a write from one slave may not be immediately
visible on all other slaves.
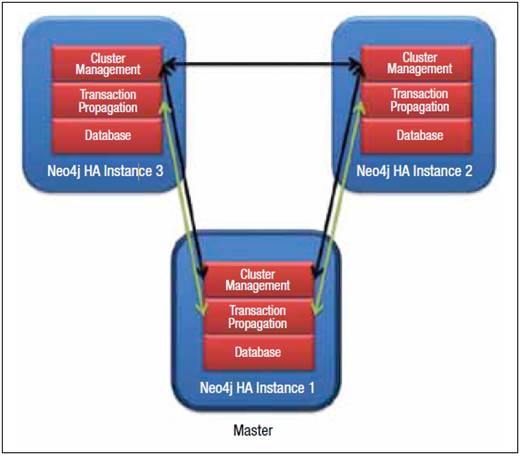
Figure
4: HA in Neo4J
FlockDB
FlockDB is an open source, fault-tolerant,
and distributed graph database licensed under the Apache license for managing
data on the Web scale. Twitter used it to build the user database and manage
relationships. It can be efficiently used in high-throughput and low-latency
environments. FlockDB was created by Twitter for relationship-related
analytics. This database stores graph data that is optimized for very large
adjacency lists, and quick reads and writes, but is not optimized for graph
traversal operations.
In FlockDB, graphs are stored as sets of
edges between nodes, which are identified by 64-bit integers. Each edge between
nodes is also marked with a 64-bit position. Edges can be used for sorting. For
social graphs, integer node IDs will be user IDs, while in a graph containing
favorite tweets, the destination will be a tweet ID.
Key-value stores
Key-value stores store simple key-value
pairs, similar to a traditional hash table. The data retrieval paradigm is
simple in key/value stores; given a key, they return the value.
Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is an open source
distributed DBMS, and an Apache Software Foundation project under the Apache
License (version 2.0). It is designed to handle enormous amounts of data spread
out across many commodity servers, in traditional or cloud environments, while
providing a highly available service with no single point of failure. It is a
NoSQL solution that was developed by Facebook, and is now used by companies
that have large, active datasets such as eBay, Twitter, Reddit, Cisco, OpenX,
Digg, etc.
Features include scalability,
fault-tolerance, MapReduce support, and a decentralized architecture.
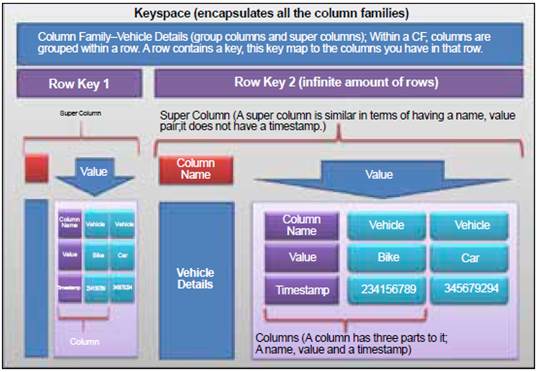
Figure
5: Data model in Cassandra
Voldemort
Voldemort is a distributed key-value data
store used at LinkedIn for high-scalability storage problems, when simple
functional partitioning is not sufficient. It is named after the very popular
fictional character from the Harry Potter series – the villain, Lord Voldemort.
Voldemort contains in-memory caching with the storage system; hence a separate
caching tier is not needed. It supports horizontal scalability for reads and
writes. It is more of a fault-tolerant hash table. Its features are:
§
High availability and horizontal scalability for
O/R mappers, such as hibernate and active-record
§
Support for distribution across data centers
that are far apart, by pluggable data placement strategies
§
Automatic data replication over a large number
of servers
§
Versioned data items to maintain and maximize
data integrity
§
Transparent failure handling.