Cooling device and noise
Nvidia has made efforts to improve the
cooling system for a top graphics card so by considering the increased final
width of the GPU to the heatsink. There are 3 major improvements mentioned by
Nvidia: a steam chamber, a heatsink with aluminum with a large number of foil radiators
and an adjusted fan system.

Three
improvements in the cooling system
It is especially daunting when you want to
disassemble the cooling device of the Titan because it is protected with screws
of the same type.

The
cooling device
Thus, the cooling device is placed in a
metal frame with thermal pads. This frame cools the memory chips and the
components of the system. Beneath the shell is the aluminum radiator with a steam
chamber.
It alone is protected in the GPU and is not
related to the other cooling components.

The
cooling device
This cooling device has a centrifugal
exhaust fan with a plastic surface for decoration:

The
centrifugal fan and the plastic surface
We cannot remove the fan because it seems
to be sticking with its metal frame besides being tightened with screws.
The highlighting system of the cooler does
not look very bright, but it is very nice:

The
cooling device when operating
The operation process of the cooling device
depends on the GPU Boost 2.0 technology mentioned above and the critical
temperature of the GPU is 800C. The clock speed of the GPU is directly
dependent on the temperature.
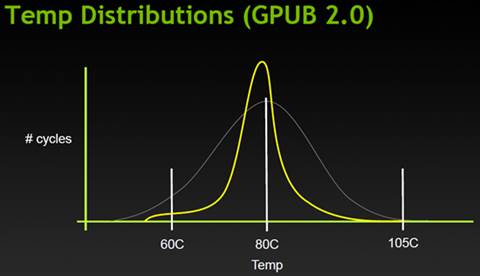
The
temperature distribution graph
After exceeding the critical temperature,
the increased clock speed is lowered at a steady rate until it reaches the base
speed of the GK 110 chip. When at 1050C, the card switches to protection
mode, known as an active regulator. Thus, the Titan GPU’s performance varies
depending mainly on temperature.
You can raise the temperature limits of the
GPU to 940C using the EVGA Precision X Utilities:

Temperature
distribution when using EVGA Precision X
This will keep the Titan operate more at
higher frequencies, but as soon as the limit reaches the temperature, the clock
speed will drop again. This is a chart from Nvidia that illustrates the
correlation between performance and the GPU temperature of the Titan:

The
chart that shows the correlation between performance and temperature
The speed of the fan on the cooler is
adjusted in such a way to keep the graphics card work silently until the GPU reaches
800C. Then the fans begin to speed:

The
fan’s process of speeding up
As you can see, Nvidia emphasizes the
silence rather than temperature, based on the design and protection of the GPU and
the GPU Boost 2.0 technology.
If the temperature limit changes, the fan
cooling device will work with high-speed in order to maintain stability.

The
fan’s process of speeding up
To test the efficiency of the cooling
device, we conducted five consecutive attempts with Aliens vs Predator game
(2010) with the installation of the highest quality images with a resolution of
2560x1440 and 16x anisotropic filtering, and the ability to reduce aliasing in
the graphics is 4x MSAA. We used MSI Afterburner GPU-Z 3.0.0 and 0.6.7 as the
control tools. The test was performed in a closed system at room temperature of
250C.
Let's take a look at the temperature of the
graphics card and power at the critical temperature of its default. Fans are
adjusted automatically:

Temperature
test results
As you can see, the GPU quickly reached 800C
in the first round of the test. Then the clock speed rose, to 1,006 MHz (that
is, an increase compared to 1,006 MHZ 867 MHz), and then dropped to 993 MHz to
876 MHz and then finally the basic speed got 837 MHz. In other words, if the
GPU exceeds 800C, the regime will not improve the speed of the Titan’s clock.
For the fan speed, it increases from 1,100 RPM to 2,412 RPM and then remains at
this level.
Now we try to raise the critical
temperature to 940C and set the power level limited to 106%. Fans
have been adjusted automatically:

Temperature
test results
It’s a completely different picture. Other
than reaching the top speed of 1006 MHz, our Titan only reduced the clock speed
to 993 MHz and maintained it during the testing process. Of course, the Titan would
generate a higher level of performance than the current mode setting to
minimize noise levels. The highest temperature of the GPU was 870C
during testing while the fan speeded up from 2,412 RPM to 2,995 RPM.
Now, we set the temperature limit and the
power at their default (800C and 100%), but will put the fan at full
speed and proceed the experiment:

Temperature
test results
No difference in clock speed was found but
the highest temperature of the GPU was 20C higher, at 720C.
To sum up everything, we can say that the
GeForce GTX keep cool Titan is extremely important if you want a GPU creates a
high level of performance in 3D applications.
We cannot measure the noise level of the
GeForce GTX Titan because we do not remove the cover (rip out irrelevant
results) and cannot drill through the crust to reach the fan connections. It is
not suitable choice for us both, so we are only limited to the impressions
subjective opinion of us alone.
The card works in all quiet 2D mode, the
fan is operating at a rate of 1100 RPM. It is really quiet. In 3D mode, the Titan
is very pleasant in its default configuration. The fan works smoothly when
increasing or decreasing its speed. When it is higher than the speed of 2500
RPM, the GeForce GTX Titan starts a sound that could be heard over the noise of
the computer environment, but it is still very quiet, such as, for the GTX 690
with dual processors or the original AMD Radeon HD 7970. In general, the
cooling system is not too loud for a graphics card with a TDP of 250 watts,
which is very surprising.