New platform
Introduced to be the convergence of the fourth-generation
Core CPUs, the new desktop platform Lynx Point owns more important innovations.
A rule has been set for Intel to release a new generation of chipset together
with new CPU microarchitecture. Some chipsets, for example the Z68 and Z77, are
backwards compatible with the previous CPU generations while the other are not,
but in general, Intel is on its way to upgrade the platform and the whole
infrastructure together with each new fundamental microarchitecture (the “took”
cycle), and the we can see it here.

Haswell
Desktop Processor 1H’13
Haswell CPU desktops which are designed in
LGA1150 require a mainboard that have a compatible CPU socket. This mainboard
might be built based on Intel’s new 8th generation chipset.

Lynx
Point Chipset Overview
This traditional chipset generation
includes some changes that target different market segments, but the Z87 is the
ultimate version in terms of features and functions. It provides a full wide
range of controls and interfaces which can divide the PCIe3.0 lanes for
multi-GPU configurations and do not prevent you from overclocking the CPU. We
will use Z87 to have a closer look at what the new platform can do.

The
main differences
The Z87 is just slightly different from the
Z77 from the very first look as both even use the same bus DMI 2.0 with PCI
Express protocol to connect the CPU. In practice, Intel just enhanced chipset’s
connectivity ability, so the Z87 supports six USB 3.0 ports instead of four,
and all of its six SATA ports are 6 gigabit/s.

Intel
8 Series Chipset
By this way, bear in mind that the Thunderbolt
is no longer mentioned in Z87 profiles, but this does not mean that the
Thunderbolt is not supported by the LGA1150. We will definitely realize that
Thunderbolt allows LGA1150 mainboard in a very near future. However, Intel
seems to lose its power in this technology as there are not much recognition
for this company in the last two years.
At first glance, replacing the sockets with
a new LGA1150 might be a little like an artificial measure. However, this is
not really like that. Just like a problem in practice, there are some important
differences in the LGA1150 which excuse for this changes, although they are not
very seemingly obvious.
Intel has changed the way the monitor
connected with the CPU integrated graphics core. The CPU itself is now in
charge of the digital interfaces (like DisplayPort, HDMI and DVI), the chipset
just supports similar VGA connectors. This solution helps reducing the loading
on FDI graphics connections between the CPU and the chipset and letting the
Lynx Point platform support up to 3 digital screens with the resolution of 4K
simultaneously.

The
display parameters
Well, this is still not the main focus of
the whole affair with the new CPU socket and the new mainboard. The most
important thing is that the platform design has been modified in order to
increase the overall level of CPU integration once again. The Core series CPUs have
uniformed all of the chipset’s North Bridge accessories for quite a long time,
and the Haswells gets down to absorbing the voltage regulation, one of the
mainboard’s components.
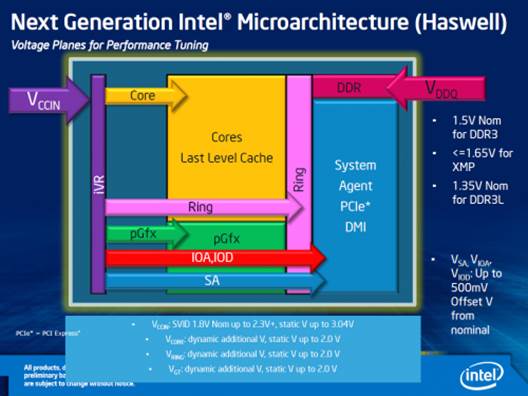
The previous generation’s CPUs need six
different voltage levels providing by the mainboards for their different
subunits: the x86-core, the cache memory, the system agent and graphics core. The
Haswell now takes that responsibility, with just two voltages from the
mainboards: the basic input voltage is 1.8 volt and the memory voltage. Other
voltage conversions and voltage regulation inside the CPU are now conducted
without any interference from the mainboards.
The
next generation’s microarchitecture
This combination makes the CPU much more
flexible in providing dynamic voltages and saving power and also simplifies the
designation of LGA1150 mainboards. It is a beneficial scenario. Mainboard
manufacturers are now able to make their products simpler. The CPU is now more
reliable, stable and accurate in terms of regulating the voltages without varying
in specific implementing. Intel also promises an integrated regulator to be
very precise, controlling voltage fluctuation in the range of some mV error. The
users can access into the voltage controller’s parameter of the integrated CPU
just as before.
Leading role: Intel Core i7-4770K processor
A Core i7-4770K processor would be used in
our practical exploration of the Haswell series and LGA1150 platform. This is the
most senior model in this product series, which means that it can replace the
senior Core i7-3770K (Ivy Bridge) after one year in the most senior office
applications from Intel.

4th
Gen Intel Core i7
The interesting things here are that the
quad-core CPUs are mentioned to have many similarities although they belong to
different generation: Turbo Boost, Hper-Threading and cache (64KB L1 for each
core, 256KB L2 for each core and sharing the L3 cache memory of 8MB). That’s
why we are curious to explore the differences between the Core i7 4770K and the
Core i7 3770K in all performance aspects that are likely to be caused by the
innovations of the microarchitecture.

The
CPU-Z
The peak clock rate that Core i7-4770K can
work at thanks to the Turbo Boost is 3.9 GHz. The CPU reaches the clock rate of
3.9 GHz if only one or two of its cores are used by itself. When three cores
are used, the clock rate is just 3.8 GHz and when the load is full, the clock
rate falls to 3.7 GHz. In idle mode, the Core i7-4770K reduces its clock rate
to 800 MHz, which is two times lower compared to the idle mode of the previous
generation’s products.
As promised, the clock rate of the L3 cache
memory varies independently of the x86 cores but still matches in practice. Asynchronous
status of the uncore part of the CPU is just recorded when it is in the power
saving or in Turbo mode.
The voltage of our x86 cores of the Core i7
4770K is 1.06V, which is typical for the 22nm CPUs.
Intel has given its fourth generation
processor core a new colorful packaging.

CPU
packaging
The CPU containing box has two versions:
with or without the heatsink. In our opinion, the second version would be
better as the old LGA1155/1156 coolers are not completely compatible with the
LGA1150.