Power consumption and heat dissipation
Haswell microarchitecture features many
optimized solution for lower power consumption level so many people expect that
Haswell CPU will help them saving more power. That expectation, actually, is
not well-grounded. The Haswell can be used to create the mobile CPU which
dissipates less heat compared to Ivy Bridge products. The ultra-low-voltage U
and Y is a perfect example as it their TDP is just 15 watt or lower. However, a
CPU design, which is optimized for low heat dissipation and power consumption,
does not need to translate into an economical desktop CPU. Just like a
practical problem, TDP of Haswell CPU for desktop is about 84 watts, which is 7
watts higher than the Ivy bridge series. It means that when working at typical
speed of CPU desktop, Haswell requires higher voltage on specific CPU subunits.
Moreover, Haswell is capable of controlling integrated voltage, as a power-hungry
circuit needs large capacities for overclocking. That is why we have some knowledge
about saving power of the premium CPUs of Intel.
In order to know more about the real power
consumption level of Intel Core i7 4770K, we implement a round of special tests.
The new digital units provided power from Corsair – AX760i – allow controlling
power consumed and produced, which we use positively in our tests on power
consumption level. The following charts (except for other regulation
available), show the power consumed by the whole system (except for the
monitor) measured after providing power. This is the total power consumption of
the whole system. PSU’s effects are not taken into account. The CPU is loaded
by running the 64-bit version of LinX 0.6.4 with AVX supported instructions. Moreover,
we enable Turbo mode and all of the power saving related modes to have accurate
measurement of power consumption level in idle mode: C1E, C6, Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep and AMD Cool’n’Quiet.

Power
consumed in idle mode
Core i7 4770K system is very good in saving
power in idle mode. The new power saving modes can be applied for desktops
architectures, reducing the minimum power consumption.
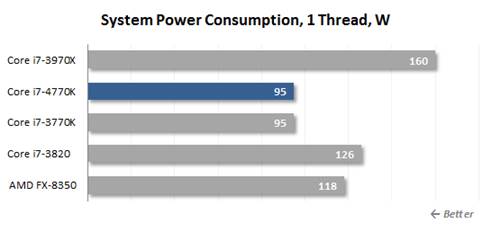
Power
consumption, 1 thread
Core i7 770K is less efficient in
single-thread load, just equivalent to Core i7 3770K, and here the next chart
comes.
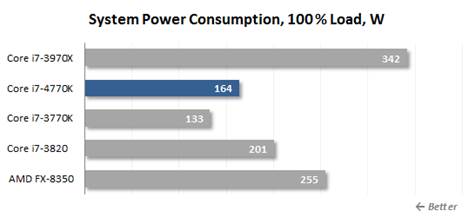
Power
consumption, 100%
It is a real shock! When the full load is
executed, the Haswell requires a power level of 30 W, which is more than the
Core i7-3770K configuration. Therefore, even though the low voltage CPU Haswell
platform, which is used for the mobile devices, is economical, their desktop
cousins are a different story.
Intel has optimized the microarchitectures
of the super-mobile applications, but the Haswell desktop is not so efficient-per-watt.
As we can see, not all of the Haswell desktops use the power in the proper way.
Despite that, there is an issue that is required a carefully calculation. The
Haswell’s power consumption and heat dissipation go up so quickly at full load which
is generated by our LinX-AVX utility.
In the actual implementation, the Core
i7-4770K is not that greedy as its predecessor. This means the power
consumption of the CPU when it is encrypting the HD video with the codec x264.

Power
consumption, x264 transcoding
Core i7 4770K reveals a higher power
consumption level. However, we no longer mention the shocking difference of 30
W: it has just falls down to a few single digits.
Thermals and Overclocking
The Haswell and the LGA1150 platform change
the overclocking procedure for two reasons. There are new divisors for the
PCIe/DMI bus and there is now a built-in voltage regulator inside the CPU.
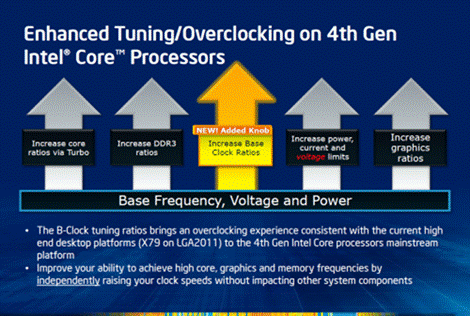
Overclocking feature
The first thing was expected because of the
fixed correlation between the base clock rate and the PCIe/DMI clock rate used
to make it impossible to overclock CPUs by raising the former. The PCIe/DMI bus
doesn’t work properly when its frequency exceeds the default 100 MHz, so
increasing the base clock rate to 105-107 MHz in order to render the LGA1155
platform nonfunctional.
This problem is solved to some aspects in
the new Haswell processors. There are now a few methods that let you customize
the base and PCIe/DMI clock rates not only as 1:1 but also as 5:4 and 5:3.
Therefore, the LGA1150 platform can be stable at a base clock rate of 100, 125
and 166 MHz. All standard internal frequencies remain at their defaults in this
case, but the x86 cores, the uncore part, the integrated graphics core and
system memory get overclocked proportionally. It is also accepted if the
LGA1150 CPUs with locked multiplier is overclocked, but only by 25% or 66%
above the default frequency.

Haswell’s
microarchitecture
Only K series CPUs with an unlocked
frequency multiplier allow you to complete overclocking freedom. By this way,
during this the transition to Haswell, Intel added yet another bit to the
processor multiplier register, so the maximum multiplier setting during
overclocking has now reached 80x.
The integrated voltage regulator inside the
CPU has an impact on the overclocking. The integrated regulator functions in a
very special way. CPU’s voltage is used to minimize the high load, however the
integrated regulator, would be automatically increase in this situation – above
0.1 volt even in the default mode. This effect is more likely to be recognized
in the overclocking.
Unfortunately, this is a typical behavior
of Haswell. You can only remove it by fixing the voltage at the default level,
this, in another words, would disable every power-saving technologies. Thus,
Haswell has provided an difficult option: you need to raise the temperature and
heat dissipation of the CPU to a high level in order to execute the automatic
increasing of the voltage inside the core, otherwise, you just completely
ignore the power-saving mode when you are standing by.
But this is only one side of the problems.
The Haswell is actually hotter than its predecessor. The maximum allowed heat
of the CPU’s core is 100o C, but even in the nominal mode of the
Core i7-4770K and there is high-performance air-cooler, its temperature has
already reached the range 75-80o.