Details of Nvidia Quadro K5000
The series of graphics cards based on
Kepler has a slightly different structure rather than the others. Typically, a
GPU manufacturer concentrates on producing a valuable feature which is the
first top-end solution and then launches less advanced modifications. Unlike
Kepler architecture, which was first implemented as the GK104 chip, absolutely
is not the top-end GPU. The GK110 GPU, the fastest chip based on Kepler, has
not been used for any graphics card, but it is used for Tesla K20 and K20X for
optimization of its low for its low-level optimization for computations as well
as certain issues Nvidia and its manufacturing partner TSMC with mass
production as sophisticated chips on 28nm technology process.
Therefore, the Kepler-based graphics cards
for gamers and professionals are now sold under the GeForce and Quadro brands
using the famous GK104 chip. So far, while there are many different gaming
cards based on the GK104, there is only one professional product of that type.
It's Quadro K5000.
As an alternate position for the
Fermi-based Quadro 5000, Quadro K5000 comes at the suggested price of $2,250,
but is actually likely to be found for about $1,800. In other words, the two
cards are able to be compared in price.
The GPU version has the same feature as the
GeForce 680; the Quadro K5000 can provide much higher performance than the
previous top versions. The GK104 chip is fully unlocked incorporating 1536 CUDA
cores that run at 706 MHz; and complementing with 4 GB of 5.4GHz GDDR5 memory.
The clock rates are significantly lower than the modern top-end gaming cards
from Nvidia, making the Quadro K5000 better in energy efficiency. It is economical
not only compared to the Kepler-based products but also to professional cards
of the previous generations.

The
table of Quadro graphics card K5000 specifications
The relatively low level of power
consumption is not only by reducing the clock rates and the lower GPU voltage
limit (now 0.975 volts). It is guaranteed by the entire Kepler architecture
which is an improvement on the Fermi in energy efficiency. Although the basic
structure of the GK104 GPU is not unlike its previous generations. It includes
a GigaThread Engine, memory controllers, L2 storage for data and instructions,
raster operators, and of course, graphics processing clusters that take
responsibility for calculating and structure mapping operations. The GPU
version used by the Quadro K5000 has four full features GPCs each of which
consists of a raster engine and two streaming multi-processors (SMXs).

GigaThread
Engine tool
The SMXs take responsibility for most of
computing done on the GPU. The computing cores are more emphasized in the
Kepler architecture and occupy a larger area of the GPU compared to the rest of
the logic, including control logic. Thus, the Kepler can be asserted to have
higher computing density than the Fermi, which is good for the professional
graphics cards that often apply the same-type instructions to the big array of
data.
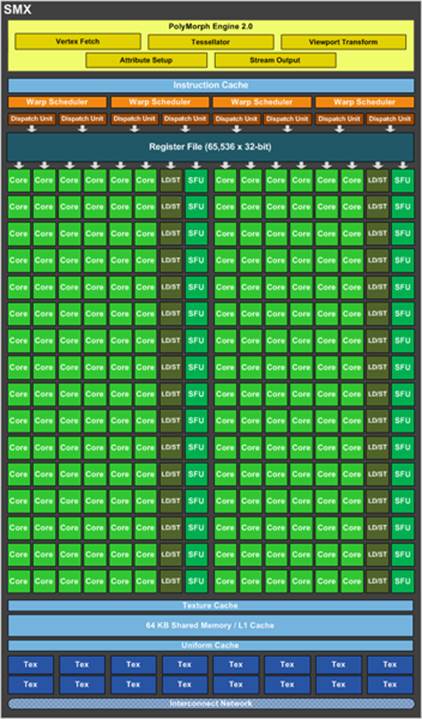
SMX
Each SMX contains 192 CUDA cores, which is
six times the number of SMS in the Fermi architecture. Although the overclock
scores are at the base clock rate (as before, is more than double), the
performance per watt is tripled. Therefore, the Quadro K5000 is not only a fast
graphics card. It is also an energy efficient solution compared to other professional
products.
In fact, the low power consumption is shown
by the outside of the Quadro K5000. While its surface is covered by its cooler,
the back side shows a short PCB we know by gaming cards of the GeForce GTX 670
series.

Gaming
Card of GeForce GTX 670 series
The Quadro K5000 is equipped with 4 GB of
memory is the difference, and so it uses all available positions for GDDR5
chips. The same with the GeForce GTX 670 is given the meaning that the
professional card employs a simple 4-phase GPU power system. It seems that it
does not need much more; however, it only has one 6-pin power connector.

Quadro
K5000

Quadro
K5000
In other words, reducing the clock rates
and voltage of the full-featured GK104 chip even makes the Quadro K5000 more
economical than the GeForce GTX 670. It is really an advantage because the
professional card not only gets lower temperature, but also makes less noise,
even at high loads. The maximum speeds of the default fans were not higher than
1,700 RPM while the GPU never heated above 800C during the trial
period. The heatsink fan of the cooler is larger than the one installed on the
GeForce GTX 680, this also contributes to efficient cooling. Note that the
cooling fan of the Quadro K5000 is a two-sided card slot with a length of 270
millimeters.
Like its gaming Kepler-based counterparts,
the Quadro K5000 is fixed with four video outputs: two DisplayPorts, a
dual-link DVI-I and a dual-link DVI-D. You can connect it up to four monitors
simultaneously; this means that double the amount of monitors supported
simultaneously by the professional cards of Nvidia’s previous generations.

Four
video outputs of the Quadro K5000
You are able to additionally increase that
number by a Quadro Sync card that helps you combine the video outputs of a few
Quadro K5000 cards installed in the same workstation. For instance, a system
with four such cards can produce a single image on a "wall" of 16
synchronous screens, and Nvidia’s Mosaic technology will replace the hassle of
configuring drivers and other software. The display wall will be determined by
the operating system as a display with ultra-high resolution.
Quadro K5000 cards can also be used in
parallel with Tesla K10, K20 or K20X computing cards. In this case, Nvidia's
Maximus technology will allow you to run the 3D models and CUDA parallel
rendering tasks on the same workstation.
Tested configuration and testing methodology
We will check the professional graphics
cards in a workstation based on the today’s fastest six-core desktop processor
– Intel Core i7-3970X Extreme Edition with the nominal frequency of 3.5 GHz.
This platform also uses the mainboard based on the Intel X79 Express and 16 GB
of high-speed DDR3-1867 SDRAM.
The Quadro K5000 on Kepler design will
compete primarily with the previous generation professional graphics cards from
Nvidia on Fermi design - Quadro 5000. Furthermore, to illustrate the
performance differences between general purpose and professional graphics
accelerators, we also mention one of the leading gaming products with the same
architecture as the Quadro K5000.
The tested configuration was shown as
follows:
·
Processor: Intel Core Core i7-3960X Extreme
Edition (Sandy Bridge-E, 6 cores + HT, 3.3-3.9 GHz, 6 x 256 KB L2, 15 MB L3).
·
Mainboard: ASUS Rampage IV Formula (LGA2011,
Intel X79 Express).
·
Memory: 4 x 4 GB, DDR3-1866 SDRAM, 9-11-9-27
(Kingston KHX1866C9D3K2/8GX).
·
Graphics cards: Nvidia GeForce GTX 680 (2
GB/256-бит GDDR5, 1006/6008 MHz); Nvidia Quadro 5000 (2.5 GB/320-бит GDDR5,
513/3000 MHz); Nvidia Quadro K5000 (4 GB/256-бит GDDR5, 706/5400 MHz).
·
Storage sub-system: Intel SSD 520 240 GB
(SSDSC2CW240A3K5).
·
Power supply unit: Corsair AX1200i (80 Plus
Platinum, 1200 W).
·
Operating system: Microsoft Windows 7 Ultimate x64.
·
Drivers: Intel Chipset Driver 9.3.0.1025; Intel
Management Engine Driver 8.1.2.1318; Intel Rapid Storage Technology
11.6.0.1030; NVIDIA GeForce Driver Release 310; NVIDIA Quadro/Tesla Driver
Release 310; NVIDIA 3ds Max Performance Driver 13.00.04.
The tests were
done in the 1920x1200 resolution with Vsync disabled. To evaluate this
experiment, we used popular CAD and 3D modeling applications and special tests
from Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC). The charts below show the
increased scores, which means that the higher score represents better
performance.