Now let's move from the basics to the
details.
Core
i3-3225
Although Core i3-3225 is not a senior model
in the Core i3 series. It is the fastest Intel CPU in this article. It's all
about market positioning: the Core i3-3225 is the closest to the AMD A10-5800K
on price as well as the fact that it offers the most advanced modification of
the HD Graphics 4000 core in the entire i3 series.
Viewed as a synthetic CPU, the Core i3-3225
is a dual core processor with Hyper-Threading support based on the Ivy Bridge
microarchitecture because it does not have Turbo Boost for x86 cores. At low
load, the clock rate can be reduced to 1.6 GHz. The total amount of L3 cache
memory shared by both x86 cores is 3 MB in each Core i3 series product, and the
Core i3-3225 is not an exception. Intel HD Graphics 4000 is the most advanced
version of Intel's integrated graphics, featuring 16 execution units. It is
clocked at 1.05 GHz, which is a mere 100 MHz, lower than the clock rate of the
same integrated graphics of quad-core Ivy Bridge processors.

Core
i3-3225
Intel CPUs have long switched to 22nm
technology process, so the Core i3-3225 has only a 54W TDP, being preferable to
senior Trinity models in terms of energy efficiency. Its low energy consumption
is indicated by its voltage, only 1.0V, while Socket FM2 APU rusn with 50%
higher voltage.
In contrast to the solution of AMD, Core i3
series do not allow to accelerate its x86 core in any way. On the other hand,
you can easily overclock the graphics core and memory module with Core i3-3225.
Core i3-3225’s specs
·
Number of cores/ Number of threads: 2/4
·
Hyprer- Threading: Yes
·
CPU frequency: 3.3 GHz
·
L3 cache: 3MB
·
Integrated graphics: HD Graphics 4000
·
Execution unit: 16
·
GPU frequency (min/max): 650/1050 GHz
·
Quick Sync: Yes
·
TDP: 55W
·
Maximum memory frequency: DDR3-1600
Core i3-3220
The single difference of the Core i3-3220
from the above-discussed Core i3-3225 is that it come with a simpler graphics
core version. Its Intel HD Graphics 2500 cores has 6 execution units instead of
16. In contrast, the Core i3-3220 and the Core i3-3225 are twin brothers that
have not only the design but also the clock rate and other parameters.

Core
i3-3220
Core i3-3220’s specs
·
Number of cores/ Number of threads: 2/4
·
Hyprer- Threading: Yes
·
CPU frequency: 3.3 GHz
·
L3 cache: 3MB
·
Integrated graphics: HD Graphics 2500
·
Execution unit: 6
·
GPU frequency (min/max): 650/1050 GHz
·
Quick Sync: Yes
·
TDP: 55W
·
Maximum memory frequency: DDR3-1600
Pentium G2120
Based on the microarchitecture, the Pentium
basically differs with the Core i3 in the lack of Hyper-Threading. In other
words, the Pentium can only execute two but not four instruction threads. In
contrast, the Pentium G2120 is quite similar to the Core i3. It is a dual core
processor with 3M L3 cache but its clock rate is 3.1 GHz. Therefore, the x86
performance of the Pentium G2120 will be much lower than the Core i3 in
multithreaded heavy load when the Core i3 can benefit from Hyper-Threading. The
only thing we should note. Pentium does not support AVX instruction set.
When it comes to graphics, Core i3 and
Pentium also have a lot in common. Although Pentium's HD Graphics core is lack
of an index number, it has the same design as the HD Graphics 2500 and has six
execution units. The clock rate is also similar. Pentium G2120 clocked its
integrated graphics core at 1:05 GHz. However, one of the main functions -
Quick Sync - is disabled in cheaper CPUs.

Pentium
G2120
Like other Intel CPU mentioned in this
article, the Pentium does not offer much in terms of overclocking. It allows to
accelerate the frequency of the integrated graphics core and support faster
memory modules DDR3-1600. However, the performance can not be increased above
the default x86 cores.
Pentium G2120’s specs
·
Number of cores/ Number of threads: 2/2
·
Hyprer- Threading: No
·
CPU frequency: 3.1 GHz
·
L3 cache: 3MB
·
Integrated graphics: HD Graphics
·
Execution unit: 6
·
GPU frequency (min/max): 650/1050 GHz
·
Quick Sync: No
·
TDP: 55W
·
Maximum memory frequency: DDR3-1600
Pentium G2020
The junior Pentium with the Ivy Bridge
architecture has clock rate at 2.9 GHz, but the only real disappointment about
the specifications is that DDR3-1333 SDRAM is listed as the highest supported
memory speed. Fortunately, this is an official announcement. Our testing showed
that the CPU’s memory controller could work with faster DDR3 SDRAM modules.
Therefore, the real single difference between the Pentium G2020 and the Pentium
G2120 is the former default clock rate lower than 7%.

Pentium
G2020
We can also note that the Pentium G2020's
voltage is smaller than 1.0V. It must represent an more economical CPU but
Intel does not emphasize this. TDP of each Pentium product series is 55W, similar
to their senior cousins.
Pentium G2020’s specs
·
Number of cores/ Number of threads: 2/2
·
Hyprer- Threading: No
·
CPU frequency: 2.9 GHz
·
L3 cache: 3MB
·
Integrated graphics: HD Graphics
·
Execution unit: 6
·
GPU frequency (min/max): 650/1050 GHz
·
Quick Sync: No
·
TDP: 55W
·
Maximum memory frequency: DDR3-1333
Celeron G1620
The dual-core Celeron processor with Ivy
Bridge design had only been introduced recently, but we still have them in this
review. Frankly speaking, there's nothing interesting about them. Intel has cut
down too many possibilities in their design. Besides disabled Hyper-Threading,
AVX and Quick Sync, as in the Pentium series, we can now see a reduced amount
of cache memory and a considerably lower clock rate. The Celeron G1620 only has
2 MB cache while its frequency is 2.7 GHz.
On the other hand, the HD Graphics core in
the Celeron G1620 is entirely similar to the Pentium's, including 6 execution
units. The actual graphics performance of Celeron will be lower due to smaller
L3 cache, which is used by the graphics core Ivy Bridge microarchitecture and
contribute a lot to solve low memory bandwidth problem. The good news is,
despite the Celeron G1620 is only officially compatible with DDR3-1333, there
is no reason it can not be used with faster memory modules.
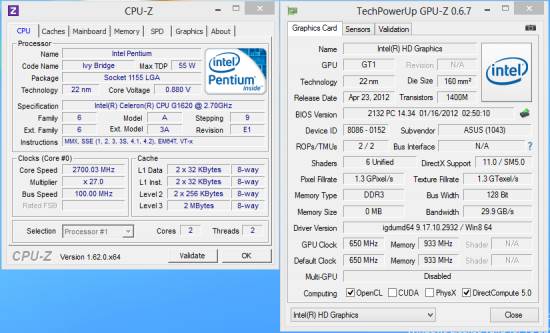
Celeron
G1620
Compared to the Core i3 processor, the
Celeron G1620 has much worse specs, its TDP is defined at 55W. It must be just
a formality. We expect the Celeron to be highly economical in real-life
applications.
Celeron G1620’s specs
·
Number of cores/ Number of threads: 2/2
·
Hyprer- Threading: No
·
CPU frequency: 2.7 GHz
·
L3 cache: 2MB
·
Integrated graphics: HD Graphics
·
Execution unit: 6
·
GPU frequency (min/max): 650/1050 GHz
·
Quick Sync: No
·
TDP: 55W
·
Maximum memory frequency: DDR3-1333