Power consumption
One of the advantages of integrated systems
is that they have low power consumption and low heat dissipation when compared
to the PC configured with discrete graphics. Platform integration is often
bought with the purpose to minimize operating costs and locate the computer in
a compact casing. That is why the developers of processors with integrated
graphics core focus on power-saving function, which is indicated by low TDP.
For example, current TDP of the Core i3, Pentium and Celeron are limited to
55W. AMD's APUs are rather worse in this respect by their TDP is set at 100 or
60W, depending on the specific model. However, the TDP parameter itself is just
a general requirement to the recommended cooling system. Things may be
different in practical case, especially when junior processor models should
actually be more economical than their senior cousins.
To find out more about the power
consumption of all tested processor models from the APU category, we made a
special round of testing. New power supply unit from Corsair - AX760i - allows
monitoring of electrical energy generated and consumed, which we flexibly use
in our power consumption testting. The chart below (unless specified otherwise)
represents the full power draw of the PC (no monitor) measured after the power
supply. It is the total power consumption of the system components. The
efficiency of the PSU is not included. CPU is loaded by running the 64bit
version of Linx AVX 0.6.4 ultility. We use FurMark 1.10.4 utilitiy to load the
graphics core. In addition, we enable Turbo mode and all power-saving
technology to accurately measure computer's power draw in idle mode: C1E, C6,
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep and AMD Cool'n'Quiet.
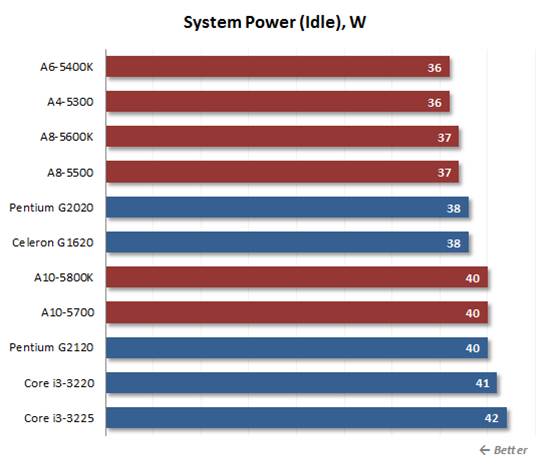
All
the processors and platforms have the same level of power consumption when
idle.
All the processors and platforms have the
same level of power consumption when idle. Every modern processor can switch to
the special power-saving mode and consumes only a few watts. t is the power
requirements of other system components and the efficiency of the mainboard’s
voltage regulator that go to the fore, concealing the actual consumption of the
processor.
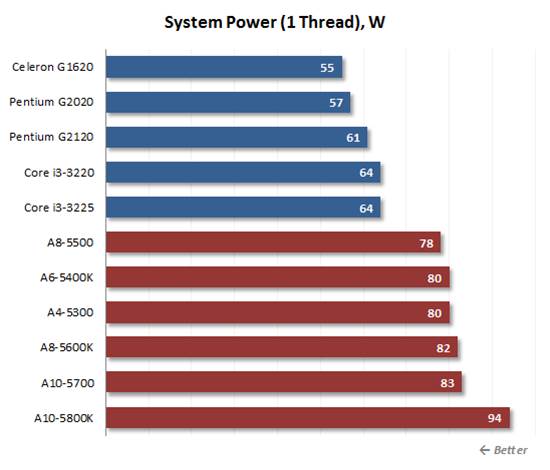
The
single-threaded computing load
The single-threaded computing load helps
rank the processors up according to their power consumption. The Core i3,
Pentium and Celeron series are rather economical whereas the Socket FM2
solutions need considerably more power. High power consumption of the AMD A10-5800K
should be pointed out: this APU released by AMD to achieve maximum performance,
so do not talk about the economy.
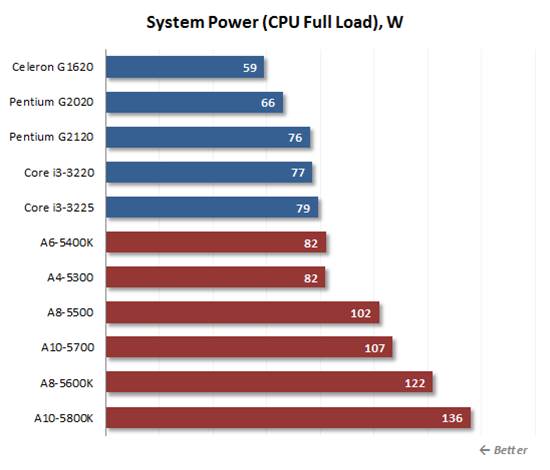
At
maximum x86 computing load we can clearly see the difference
At maximum x86 computing load we can
clearly see the difference between those solutions from the two processor
manufacturers. Intel's are more economical than AMD's. Even the slowest
dual-core A4-5300 and A6-5400K need more power than the Core i3 which are much
faster in sheer performance. A10 and A8 series with their own 100W TDP are tare
downright uneconomical compared to their Intel rivals. Their configurations
need almost twice the power of the LGA 1155 platform, although their
performance was not any better. The quad-core Trinity 65W does not really save
power, although it help you to save 20 to 30W at high load compared to its 100W
brother.
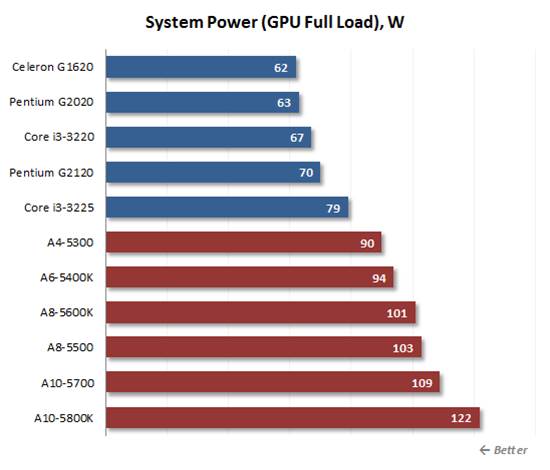
AMD’s
solutions are no better when it comes to 3D loads
AMD’s solutions are no better when it comes
to 3D loads, but the high power consumption can be justified by their
performance in this case.
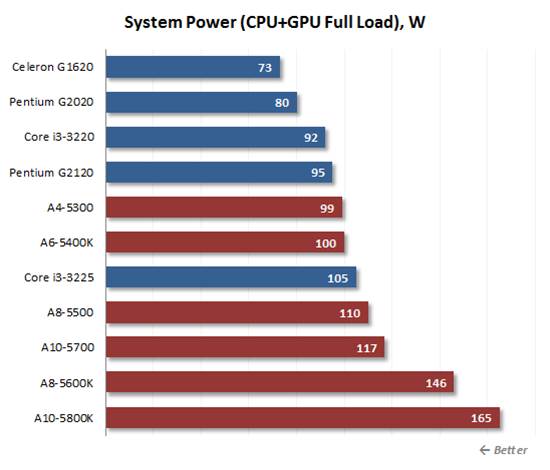
Both
the x86 and graphics cores are in use concurrently
There are no changes when both the x86 and
graphics cores are in use concurrently The A10-5800K processor and the A8-5600K
with its 100W TDP need 30 to 50W more than others in practical applications.
The platform with the Core i3-3225 (Intel HD Graphics 4000) only needs more
power than the Socket FM2 systems with dual-core Trinity APUs. Thus, the
Trinity with a TDP of 65 watts is hardly economical even compared to the Core
i3-3225. Intel's solution obviously provide better performance in watts.
Besides being more energy efficient, they are more versatile in terms of
installing them in cramped systems cases with low-wattage PSUs and low-profile
coolers.
Conclusion
Traditional CPUs should not be confused
with the APUs. The recent invented concept of hybrid processors has widely
recognized in the market, so we can approach APUs not as a variety of
conventional CPUs but as a whole new class of products. Although AMD and Intel
choose different paths to approach the targeted APU, their current products
offer the same ability to: two or four x86 cores, an integrated graphics core
DirectX 11-compatible, OpenCL 1.1 support for heterogeneous computing and
subunits used for video transcoding or decoding. On the other hand, because
each manufacturer has priority and experients different techniques, the Trinity
and Ivy Bridge are very different and distinctive in every point thanks to
their exclusive designs.
Intel's products remained unrivalled when it comes to the convetional x86 performance. The senior quad-core APU socket FM2 from the A10 và A8 series is
somewhere between the Core i3 và Pentium in terms of average performance whereas the dual-core senior A6 và A4 are
far worse then the Celeron series. AMD tried to compensate this difference in price, but
it does not always succeed. The biggest problem of the Trinity family with x86
Piledriver modules is the low performance of the individual execution cores,
which shows up in many everyday applications.
Instead, AMD can offer much
higher-performance 3D graphics with Radeon HD 7000D-class graphics cores with
VLIW4 architecture, the Trinity series are much faster than any Ivy Bridge
models when running 3D games. This is true even with the Core i3-3225 graphics
core which has the most advanced integrated Intel HD Graphics 400. In game
section, the Core i3-3225 can only compete with the AMD A6-5400K which is not
the fastest Trinity modification. Therefore, Socket FM2 configuration without
discrete graphics can be viewed as a gaming platform for new users in the same
configuration with a Core i3-3225 that can only be fixed with a lot of such
services. The other processors from the Core i3, Pentium and Celeron series of
Intel have slower versions of the integrated graphics core (HD Graphics 2500 or
HD Graphics) and cannot guarantee playable frame rates in modern games even at
low resolutions and low visual quality settings.
With high-performance 3D graphics and the
optimal architecture for streaming algorithm, AMD APU turned out to be
suprisingly good in terms of heterogeneous computing. If an application can
employ graphics core resources for computations, AMD APUs can show their very
best and deliver much higher performance compared to Intel’s CPUs. And such applications
are not so strange. OpenCL compatible software is growing, so the functionality
is implemented in many photo and video editor.
Ivy Bridge CPU nevertheless is the fastest
solution for basic video transcoding. Quick Sync technology has no rival,
Trinity's VCE turned out to be much slower. The bad news is Quick Sync is only
available in Core i3 and higher CPUs, and is supported by a limited number of
applications. This situation however may change in the near future. The release
of the Intel Media SDK 2013 paved the way for the developer community to easily
use the Quick Sync in their applications.
Intel's Solutions has another undeniable
advantage. The cutting-edge 22nm tech process employed for the Ivy Bridge
series and numerous microarchitecture optimizations make the LGA1155 platform
much more economical compared to same-class Socket FM2 systems. So the Core i3,
Pentium and Celeron products seem to be more appropriate for compact computers
or when power saving is a top priority.